“Automating Dicentric Chromosome Detection from Cytogenetic Biodosimetry Data” at the International EPRBioDose 2013 Conference in Leiden, Netherlands (March 24-28).
Authors: Peter Rogan(1,2), Akila Subasinghe(1), Asanka Wickramasinghe(1), Yanxin Li(1), Jagath Samarabandu(1), Joan Knoll(1,2), Ruth Wilkins(3), Farah Flegal(4); (1)University of Western Ontario, (2)Cytognomix Inc., (3)Health Canada, (4)Atomic Energy of Canada Ltd., Canada.
Abstract: We are developing a prototype software system with sufficient capacity and speed to estimate radiation exposures by counting dicentric chromosomes in metaphase cells from many individuals in the event of a
mass casualty. Top-ranked metaphase images are segmented by defining chromosomes with an active contour gradient vector field (GVF), and by determining centromere locations along the centerline. The centerline is
extracted by Discrete Curve Evolution (DCE) skeleton branch pruning and curve interpolation. Centromere detection minimizes the global width and DAPI-staining intensity profiles along the centerline. A second
centromere is identified by reapplying this procedure after masking the first. Dicentrics can be identified by applying a support vector machine-based classification, which uses features that capture width and intensity
profile characteristics as well as local shape features of the object contour at candidate pixel locations. The correct location of the centromere is also refined in chromosomes with sister chromatid separation. The
overall algorithm has both high sensitivity (85%) and specificity (94%). Results are independent of the shape and structure of chromosomes in different cells, regardless of which laboratory protocol is followed or the
specimen source. The requisite throughput is being achieved by recoding MATLAB software modules for different segmentation functions in C++/OpenCV, and integrating them in the prototype. Processing of
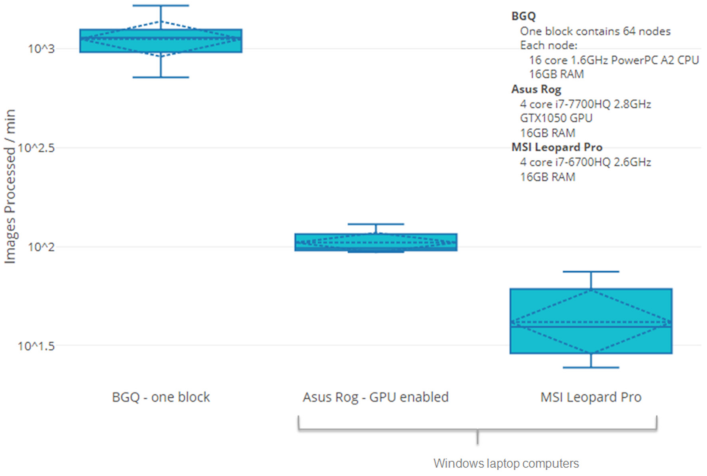
numerous images is accelerated by both data and task software parallelization with the Message Passaging Interface and Intel Threading Building Blocks as well as an asynchronous non-blocking I/O strategy. Relative
to a serial process, metaphase ranking, GVF, and DCE are respectively 100 and 300 fold faster on an 8-core I7-based desktop and on a 64-core shared memory cluster computer. Extrapolation from these benchmarks to
a 64-core system in which all of the software modules have been integrated indicates that it should be feasible to process metaphases for dicentric chromosomes from 1000 specimens in 20 hours.